The prime 41, can be written as the sum of six consecutive primes: 41 = 2 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 11 + 13
This is the longest sum of consecutive primes that adds to a prime below one-hundred.
The longest sum of consecutive primes below one-thousand that adds to a prime, contains 21 terms, and is equal to 953.
Which prime, below one-million, can be written as the sum of the most consecutive primes?
This is my solution in Golang – Go routines with a channel to pass back the prime and number of consecutive primes used to summate could speed up execution by concurrency.
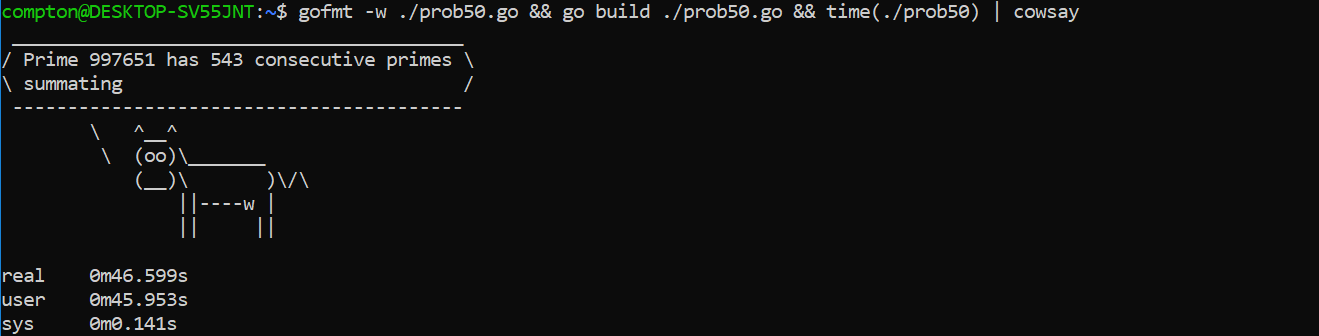
package main
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
import (
"fmt"
)
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
func main() {
maxPrime, consecNumb := 0, 0
primeList := sieveOfErastothenes(1000000)
for p := 0; p < len(primeList); p++ {
consecNumbBuff := primeSumCheck(primeList, primeList[p])
if consecNumbBuff > consecNumb {
consecNumb = consecNumbBuff
maxPrime = primeList[p]
}
}
fmt.Printf("Prime %d has %d consecutive primes summating", maxPrime, consecNumb)
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
func sieveOfErastothenes(maxVal int) []int {
var sieve [maxVal]bool
for i := 2; i < 1000000; i++ {
if sieve[i] == false {
for j := i * 2; j < 1000000; j += i {
sieve[j] = true
}
}
}
primeList := make([]int, 0)
for i := 1; i < 1000000; i++ {
if sieve[i] == false {
primeList = append(primeList, i)
}
}
return primeList
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
func primeSumCheck(primeList []int, p int) (sumCount int) {
for i := 0; i < len(primeList); i++ {
flag := false
sumBuff := 0
countBuff := 0
if float64(primeList[i]) > (.5 * float64(p)) {
return sumCount
}
for j := i; flag != true; j++ {
sumBuff += primeList[j]
countBuff += 1
if sumBuff == p {
if countBuff > sumCount {
sumCount = countBuff
}
flag = true
}
if sumBuff > p {
flag = true
}
}
}
return sumCount
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
