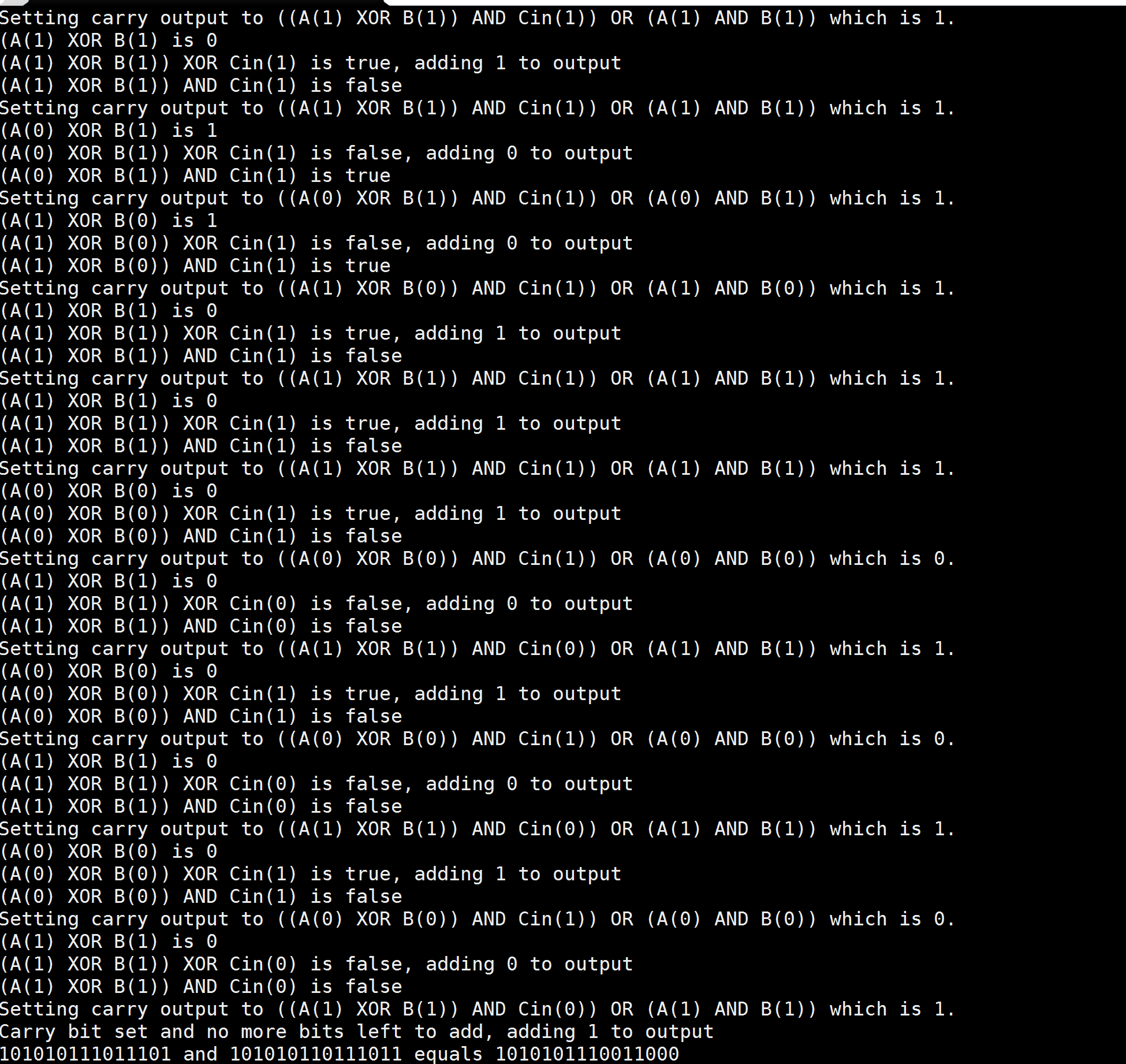
A full adder simulation implementation in C++. It is implemented with a “adder queue” as part of the assignment prerequisites was adding 8 binary strings to a buffer for adding.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Function Prototypes
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
std::string fullAdder(std::vector<std::vector*> adderIn);
int userActivity(std::string stringBuff[9],
std::vector<std::vector*> &adderInput);
void fullAdderRecurs(std::vector<std::vector*> adderIn, bool &carry,
std::string &outputString);
void calculateSums(std::string stringBuff[9],
std::vector<std::vector*> adderInput,
std::vector<std::vector*> inputBuffer);
bool andGate(bool P, bool Q);
bool orGate(bool P, bool Q);
bool xorGate(bool P, bool Q);
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
int main(void)
{
std::string stringBuff[9];
bool finish = false;
std::vector<std::vector*> inputBuffer;
std::vector<std::vector*> adderInput;
if(userActivity(stringBuff, adderInput) == -1)
{
return -1;
}
calculateSums(stringBuff, adderInput, inputBuffer);
// clean up
for(int i = 0; i < adderInput.size(); i++)
{
delete adderInput[i];
}
return 0;
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
int userActivity(std::string stringBuff[9],
std::vector<std::vector*> &adderInput)
{
for(int i = 0; i <= 7; i++)
{
std::cout << "\nPlease enter the " << (i+1) << " number now.\n";
// If it is odd, I know there is one behind it to compare against
if((i & 0x1))
{
std::cout << "This number will be added to " << stringBuff[i-1]
<< "\n"; } std::cin >> stringBuff[i];
// Check for one byte length of input
std::cout << "Adding " << stringBuff[i] << " to adder queue\n";
// Create a new vector representing the input stream
adderInput.push_back(new std::vector);
/*
Iterate through the string, turning 0's and 1's into true and false
If a non binary symbol is detected, return -1 and exit
*/
for(auto it = stringBuff[i].begin(); it != stringBuff[i].end(); it++)
{
if((*(it)) == '0')
{
adderInput[i]->push_back(false);
}
else if((*(it)) == '1')
{
adderInput[i]->push_back(true);
}
else
{
std::cout << "Erroneous input - input that is"
<< " not a 0 or a 1 detected.\n";
return -1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
std::string fullAdder(std::vector<std::vector*> adderIn)
{
// Set the initial carry value to false
bool carry = false;
std::string returnString;
// If there is a difference in string length, append 0's until same
int dif = (adderIn[0]->size() - adderIn[1]->size());
// If it is less than 0, we know the first element is smaller
if(dif < 0) { while(dif != 0) { adderIn[0]->insert(adderIn[0]->begin(), false);
++dif;
}
}
// If it is greater than 0, we know the second element is smaller
else if(dif > 0)
{
while(dif != 0)
{
adderIn[1]->insert(adderIn[1]->begin(), false);
--dif;
}
}
// Begin recursive adding
fullAdderRecurs(adderIn, carry, returnString);
// Big endian is the better of the two schemas, clearly... so
std::reverse(returnString.begin(), returnString.end());
return returnString;
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void fullAdderRecurs(std::vector<std::vector*> adderIn, bool &carry,
std::string &outputString)
{
// end is used instead of rbegin due to erase expecting an iterator
// firstIt is A, secondIt is B
auto firstIt = (adderIn[0]->end() - 1);
auto secondIt = (adderIn[1]->end() - 1);
bool S, buff;
// Represents A XOR B
buff = xorGate((*(firstIt)), (*(secondIt)));
std::cout << "(A(" << (*(firstIt)) << ") XOR B(" << (*(secondIt))
<< ") is " << buff << "\n";
std::cout << "(A(" << (*(firstIt)) << ") XOR B(" << (*(secondIt))
<< ")) XOR Cin(" << carry << ") is ";
// Represents XOR gate before S
if(xorGate(carry,buff))
{
std::cout << "true, adding 1 to output\n";
outputString += "1";
}
else
{
std::cout << "false, adding 0 to output\n";
outputString += "0";
}
// Reuse buff to represent the result of the upper AND gate
buff = (carry && buff);
std::cout << "(A(" << (*(firstIt)) << ") XOR B(" << (*(secondIt))
<< ")) AND Cin(" << carry << ") is ";
if(buff)
{
std::cout << "true\n";
}
else
{
std::cout << "false\n";
}
// Evaluate lower AND gate, and OR gate, to determine carry out
std::cout << "Setting carry output to " << "((A(" << (*(firstIt))
<< ") XOR B(" << (*(secondIt)) << ")) AND Cin(" << carry
<< ")) OR (A(" << (*(firstIt)) << ") AND B(" << (*(secondIt))
<< "))" << " which is ";
carry = orGate(buff, andGate((*(firstIt)), (*(secondIt))));
std::cout << carry << ".\n"; // Remove the two binary values that were added to advance through string
adderIn[0]->erase(firstIt);
adderIn[1]->erase(secondIt);
// If there are no more bits left to iterate, end recursion
if((adderIn[0]->size() == 0))
{
// If carry bit is set, add 1 to string on the way out of recursion
if(carry)
{
std::cout << "Carry bit set and no more bits left to add, "
<< "adding 1 to output\n";
outputString += "1";
}
else
{
std::cout << "No more bits left to add\n";
}
return;
}
// Recurse, and advance through the string due to the erases on ln161/162
else
{
fullAdderRecurs(adderIn, carry, outputString);
}
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Per assignment prerequisite, routines implementing the various gates
bool andGate(bool P, bool Q)
{
return (P && Q);
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
bool orGate(bool P, bool Q)
{
return (P || Q);
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
bool xorGate(bool P, bool Q)
{
return (P ^ Q);
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void calculateSums(std::string stringBuff[9],
std::vector<std::vector*> adderInput,
std::vector<std::vector*> inputBuffer)
{
// Push the first two values onto a vector to pass into the fullAdder
inputBuffer.push_back(adderInput[0]);
inputBuffer.push_back(adderInput[1]);
std::cout << "\n\n\nAdding " << stringBuff[0] << " and "
<< stringBuff[1] << "\n\n\n";
// Set the 8th stringBuff element equal to the sum of the first two elements
stringBuff[8] = fullAdder(inputBuffer);
std::cout << stringBuff[0] << " and " << stringBuff[1] << " equals "
<< stringBuff[8] << "\n\n\n";;
// Clear the input buffer and prepare for next elements
inputBuffer.clear();
// Repeat same as above with next two bit vectors
inputBuffer.push_back(adderInput[2]);
inputBuffer.push_back(adderInput[3]);
std::cout << "\n\n\nAdding " << stringBuff[2] << " and " << stringBuff[3]
<< "\n\n\n";
stringBuff[8] = fullAdder(inputBuffer);
std::cout << stringBuff[2] << " and " << stringBuff[3]
<< " equals " << stringBuff[8];
inputBuffer.clear();
inputBuffer.push_back(adderInput[4]);
inputBuffer.push_back(adderInput[5]);
std::cout << "\n\n\nAdding " << stringBuff[4] << " and " << stringBuff[5]
<< "\n\n\n";
stringBuff[8] = fullAdder(inputBuffer);
std::cout << stringBuff[4] << " and " << stringBuff[5]
<< " equals " << stringBuff[8];
inputBuffer.clear();
inputBuffer.push_back(adderInput[6]);
inputBuffer.push_back(adderInput[7]);
std::cout << "\n\n\nAdding " << stringBuff[6] << " and " << stringBuff[7]
<< "\n\n\n";
stringBuff[8] = fullAdder(inputBuffer);
std::cout << stringBuff[6] << " and " << stringBuff[7]
<< " equals " << stringBuff[8];
return;
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////