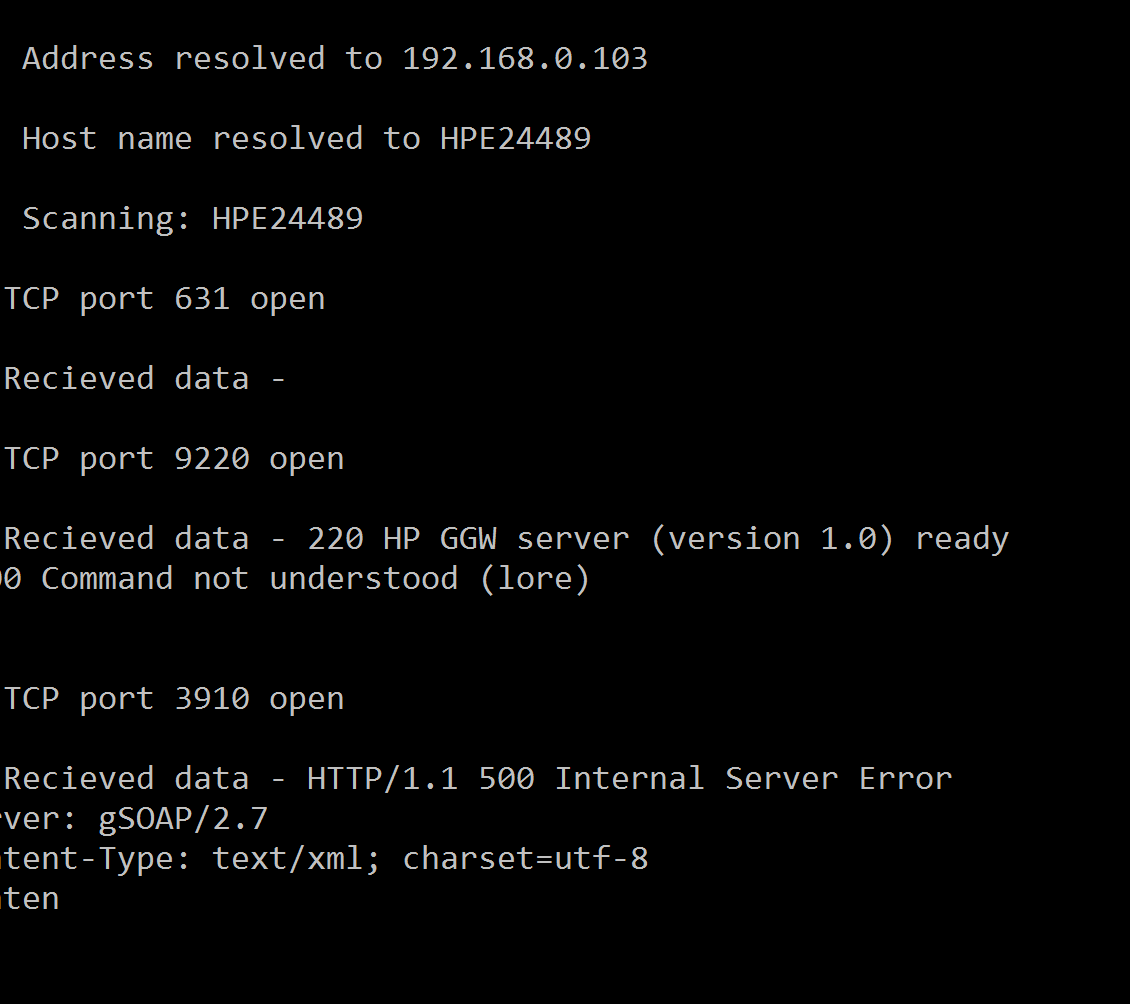
 This is a basic port scanner implementation in Python; it attempts to connect to the given ports of the specified host (all ports, if none indicated), and outputs to a text file and to the console if a given port is open – if it is, it then attempts to retrieve information about what is running on the port by sending “loremipsum”, and outputting the recieved information.
This is a basic port scanner implementation in Python; it attempts to connect to the given ports of the specified host (all ports, if none indicated), and outputs to a text file and to the console if a given port is open – if it is, it then attempts to retrieve information about what is running on the port by sending “loremipsum”, and outputting the recieved information.
#####################################################################
import optparse
import sys
from threading import *
from socket import *
#####################################################################
wait = Semaphore(value=1)
openCount = 0
closedCount = 0
#####################################################################
def connectionScan(targetHost, targetPort, outFileOpen, outFileClosed):
try:
s = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM) # connect to IPv4 socket
s.connect((targetHost, targetPort)) # open connection to see if recv
s.send('loremipsum\r\n') # send data
banner = s.recv(200)
wait.acquire()
print "\n[+]TCP port %d open" % targetPort
print "\n[+]Recieved data - %s" % str(banner)
print >> outFileOpen, "\n[+]TCP port %d open" % targetPort
print >> outFileOpen, "\n[+]Recieved data - %s" % str(banner)
++openCount
s.close()
except:
wait.acquire()
print >> outFileClosed, "\n[-]TCP port %d closed" % targetPort
++closedCount
pass
finally:
wait.release()
sys.exit()
#####################################################################
def portScanner(targetHost, targetPorts, outPath):
threads = []
outFileOpen = open(outPath+"open.txt","w")
outFileClosed = open(outPath+"closed.txt","w")
try:
targetAddress = gethostbyname(targetHost) # attempt to resolve host
print "\n[+] Address resolved to %s" % targetAddress
except Exception as e:
print "\n[*] Address unresolved"
print "Error:", e
sys.exit()
try:
targetName = gethostbyaddr(targetAddress)
print "\n[+] Host name resolved to %s" % targetName[0]
print "\n[*] Scanning: %s" % targetName[0] # Print target
except:
print "\n[-] Unable to resolve %s" % targetAddress
print "\n[*] Scanning: %s" % targetAddress
for targetPort in targetPorts:
t = Thread(target=connectionScan, args =(targetHost, int(targetPort), outFileOpen, outFileClosed))
threads.append(t)
for process in threads:
process.start()
for process in threads:
process.join()
outFileOpen.close()
outFileClosed.close()
#####################################################################
def main():
lineIn = optparse.OptionParser('usage %prog -H' +\
' -P ')
lineIn.add_option('-H', dest='targetHost', type='string', \
help='indicate the target host')
lineIn.add_option('-P', dest='targetPort', type='string', \
help='indicate the target ports, if none then all possible ports selected')
(options, args) = lineIn.parse_args() # parse options
targetHost = options.targetHost # assign target host
targetPorts = str(options.targetPort).split(',') # assign target ports and strip commas
if targetHost == None:
print lineIn.usage
sys.exit()
elif (len(sys.argv) < 4):
print "\nPort options not found - defaulting to all ports"
targetPorts.pop(0)
for i in range(0,65536):
targetPorts.append(str(i))
print "Target host: %s" % targetHost
else:
print "Target host: %s\nTarget ports: " % targetHost
for port in targetPorts:
print " "+port
outPath = targetHost + "_ports"
portScanner(targetHost, targetPorts, outPath)
print "Open ports output to ./%s" % outPath + "open.txt"
print "%d scanned ports are open" % openCount
print "Closed ports output to ./%s" % outPath + "closed.txt"
print "%d scanned ports are closed" % closedCount
#####################################################################
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
#####################################################################
