#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <math.h>
// Solves for quadratic formula
std::vector quadraticCalc(double a, double b, double c);
int main(void)
{
double A = 0, B = 0, Cone, Ctwo;
std::vector<double> terms, quadBuff;
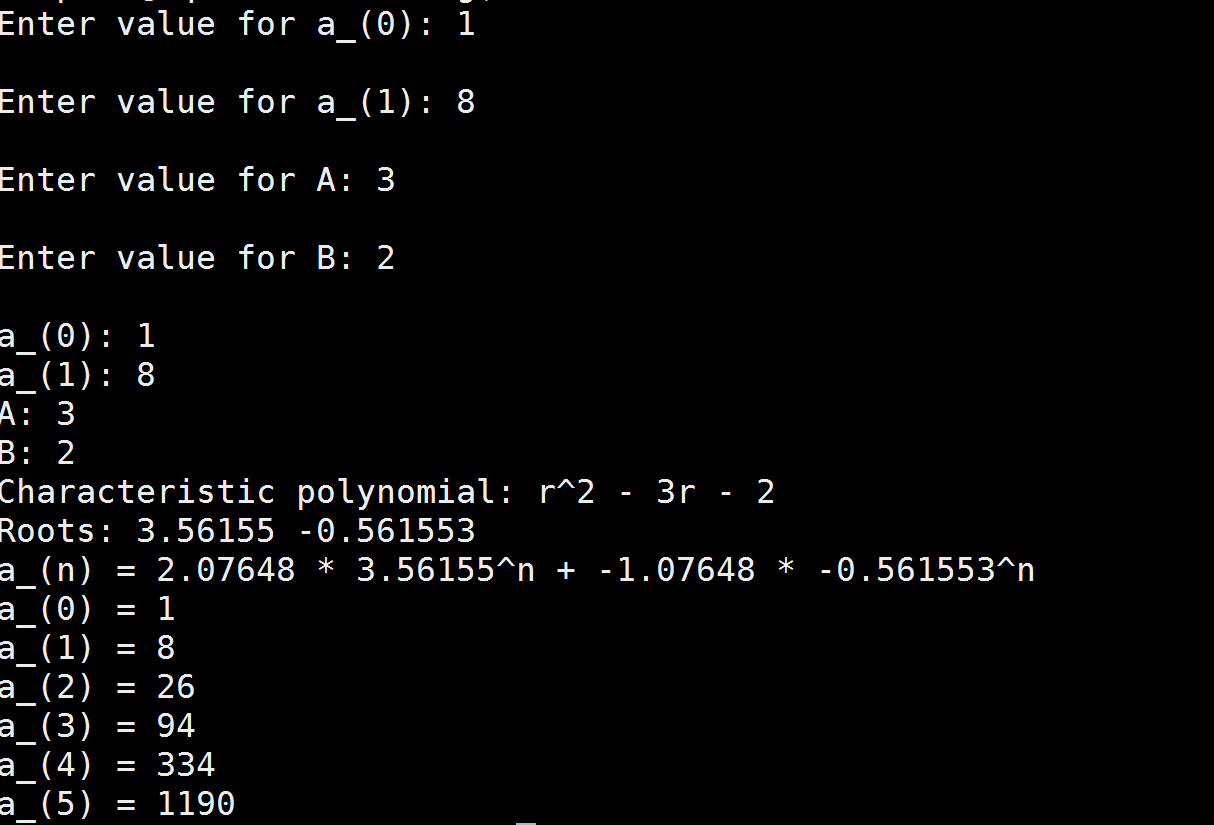
std::cout << "Enter value for a_(0): "; std::cin >> A;
terms.push_back(A);
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "Enter value for a_(1): "; std::cin >> A;
terms.push_back(A);
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "Enter value for A: "; std::cin >> A;
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "Enter value for B: "; std::cin >> B;
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "a_(0): " << terms[0] << "\n" << "a_(1): " << terms[1] << "\n" << "A: " << A << "\n" << "B: " << B << "\n";
std::cout << "Characteristic polynomial: " << "r^2 - " << A << "r - " << B << "\n";
// Calculate characteristic polynomial using quadratic formula
quadBuff = quadraticCalc(1, A, -B);
// If the roots are discrete
if(quadBuff[0] != quadBuff[1])
{
std::cout << "Roots: ";
// Output roots
for(auto rootIt : quadBuff)
{
std::cout << rootIt << " ";
}
// Set C_(2) equal to (a_(1) - r_(1)) / (r_(2) - r_(1))
Ctwo = (terms[1] - quadBuff[0]) / (quadBuff[1] - quadBuff[0]);
// Set C_(1) equal to a_(0) - C_(2), as a_(0) is equal to C_(1) + C_(2)
Cone = terms[0] - Ctwo;
// Output "formula", or a_(n) = C_(1)*(r_(1))^n + C_(2) * r_(2)^n
std::cout << "\na_(n) = " << Cone << " * " << quadBuff[0] << "^n + " << Ctwo << " * " << quadBuff[1] << "^n\n";
for(int i = 2; i < 6; i++)
{
terms.push_back((Cone * pow(quadBuff[0], i)) + (Ctwo * pow(quadBuff[1], i)));
}
}
// It is a repeated root
else
{
std::cout << "Root: " << quadBuff[0] << std::endl;
std::cout << "a_(n) = C_(1)" << quadBuff[0] << "^n + C_(2)n" << quadBuff[0] << "^n\n";
// C_(1) = a_(0)
Cone = terms[0];
std::cout << "C_(1) = " << Cone;
// a_(1) = C_(1)*r + C_(2)*r, where r is the repeated characteristic polynomial root
Ctwo = terms[1] - (Cone * quadBuff[0]);
Ctwo /= quadBuff[0];
std::cout << "C_(2) = " << Ctwo;
for(int i = 2; i < 6; i++)
{
// Solve for C_(1)r^n + C_(2)nr^n
terms.push_back((Cone * pow(quadBuff[0], i)) + (Ctwo * i * pow(quadBuff[0], i)));
}
}
// Output the terms
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
std::cout << "a_(" << i << ") = " << terms[i] << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
std::vector quadraticCalc(double a, double b, double c)
{
std::vector<double> roots;
double rootBuff;
// If there is a complex root
if((pow(b, 2) - (4*a*c)) < 0)
{
std::cout << "Complex root found\n Exiting now";
exit(-1);
}
// Push back the two roots
roots.push_back(-((-b) - sqrt( (b*b) - (4*a*c))) / (2*a));
roots.push_back(-((-b) + sqrt( (b*b) - (4*a*c))) / (2*a));
return roots;
}

