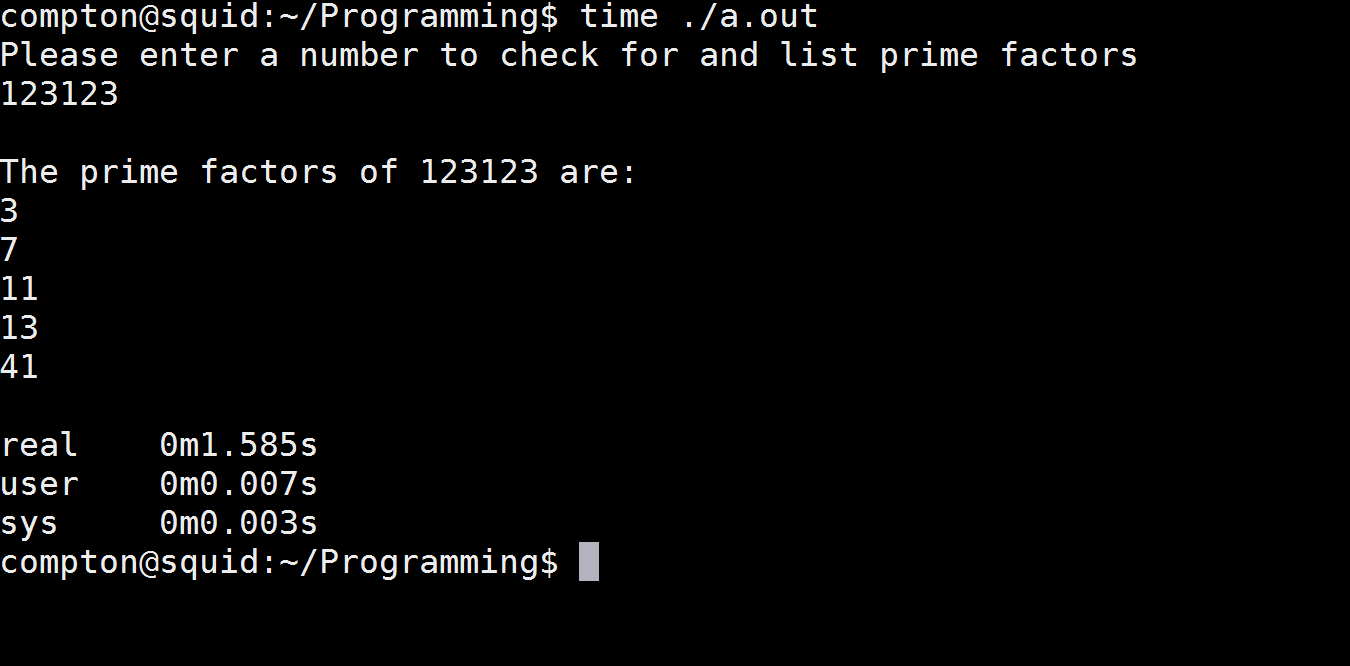
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <math.h>
#include <algorithm>
int main(void)
{
// ull is large data type to input large numbers
unsigned long long inputNumb, sieveMax;
// for holding found numbers; easy way to sort ascending
std::vector<unsigned long long> foundNumbers;
// flag for ending division in prime factorization
bool divided;
std::cout << "Please enter a number to check for and list prime factors\n";
std::cin >> inputNumb;
// Use sieveMax for both ease of reading and to save as lvalue
sieveMax = inputNumb + 1;
// Fill bit vector with 1's, indicating a prime number
std::vector<bool> numberList(sieveMax, true);
for(unsigned long long i = 3; i < sieveMax; i++)
{
if((i & 0x1) && numberList[i] == true)
{
// Iterate through list by multiples of the current sieve seed
for(unsigned long long j = (i*2); j < sieveMax; j += i)
{
// If it is currently considered prime
if((j & 0x1) && numberList[j] == true)
{
// Set it to false due to found factor
numberList[j] = false;
}
}
}
}
// Factor can't be greater than half
sieveMax /= 2;
// If it is odd (due to skipped evens) and set as true
if(((inputNumb == 2) || (inputNumb & 0x1)) && numberList[inputNumb])
{
std::cout << inputNumb << " is prime\n";
}
// If it is not prime...
else
{
std::cout << std::endl << "The prime factors of " << inputNumb << " are:\n";
// While it is still being factored
while(inputNumb != 0)
{
// Set flag for for conditions
divided = false;
// increment through prime sieve
for(unsigned long long i = 2; !divided; i++)
{
// If it is 2, or it is odd, and it is set as prime
// and modulus to 0
if( ((i == 2) || (i & 0x1)) && numberList[i] && ((inputNumb % i) == 0))
{
// Divide to continue factoring
inputNumb = (inputNumb / i);
// Push back found factor for sorting and output
foundNumbers.push_back(i);
// Break loop condition
divided = true;
}
// Sievemax is half the value of input number
else if(i > sieveMax)
{
// Set it to 0 to break while loop, as no more
// prime factors exist
inputNumb = 0;
divided = true;
}
}
}
}
// Sort the found factors ascending
std::sort(foundNumbers.begin(), foundNumbers.end());
// Iterate through the found numbers, and output
for(auto it : foundNumbers)
{
std::cout << it << "\n";
}
return 0;
}